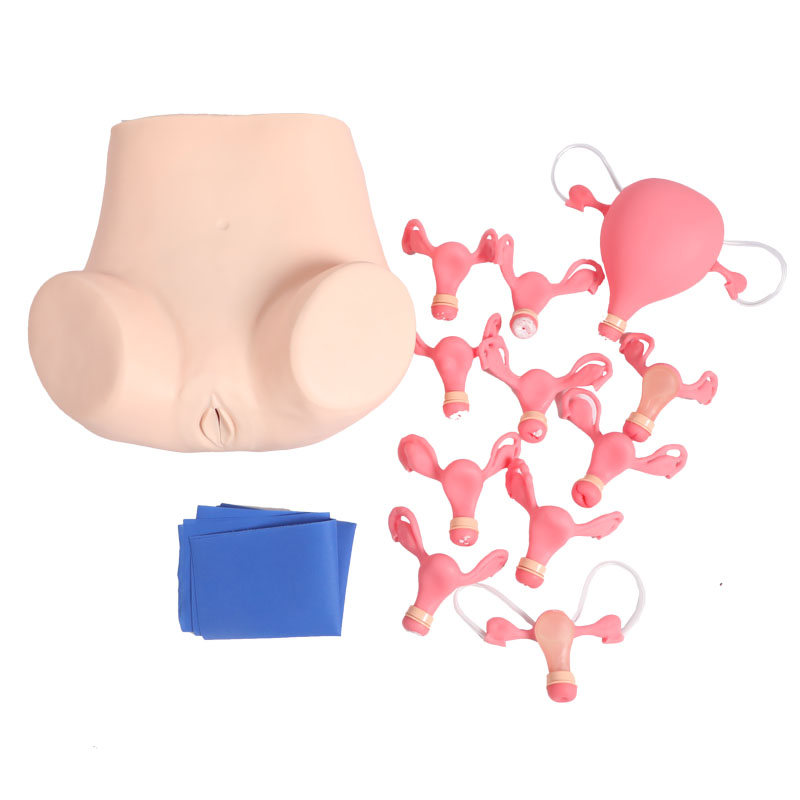
Features:
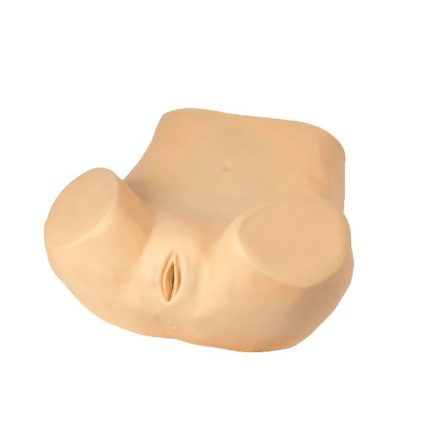
■ The model is of the lower half of the adult female torso, consisting of the abdominal and pelvic cavities. Demonstrations of the following maneuvers can be done:
-Palpation of normal and various types of abnormal uterus.
-Examination of gynecological double and triple diagnosis.
-Examination of vaginal speculum and colposcope.
-Visual observation of normal and various types of abnormal lesions of the cervix.
-Placement and removal of intrauterine device.
-Observation of the size and position of the diaphragm.
-Observation of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, round ligaments and other anatomical structures located in the pelvis.
Component parts of internal structures:
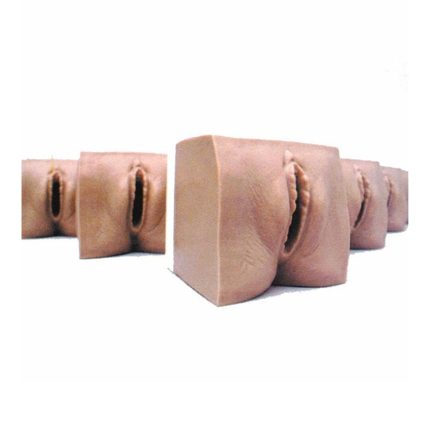
■ Model of normal and abnormal cervix
-Normal cervix
-IUD placement and removal Normal cervix
-Cervical tear
-Chronic cervicitis
-Acute cervicitis
-Inflammatory cervical disease Naboth cysts
-Trichomonas cervicitis
-Cervical condyloma acuminatum
-Cervical leukoplakia
-Cervical polyps
-Cervical adenocarcinoma
■ Normal and abnormal uterus and adnexa models
-IUD placement and removal Normal uterus and adnexa (anterior uterine opacity)
-Normal uterus and adnexa
-Uterus with pronounced anterior tilt, anterior flexion
-Uterus with pronounced retroversion and retroflexion
-Uterine fibroids
Uterus with right tubo-ovarian cysts
-Uterus with right tubal hydrosalpinx.
-Uterus with right tubal tuberculosis
-Uterus with right salpingitis
-Placement and removal of intrauterine device (IUD) with IUD guiding fork.
-Pregnant uterus (five-month-old fetus)
-Ectopic pregnancy (tubal pelvic pregnancy)
-Obstruction of the fallopian tubes